MATHEMATICS 177 CHESS
FREEDOM and SPACE in chess
|
Definition 1. The FREEDOM NUMBER of a piece is the
number of squares to which the piece can legally
move (excluding the square it currently occupies). |
|
Definition 2. The FREEDOM NUMBER OF YOUR POSITION
(at some moment during a game) is the sum of the
freedom numbers of all pieces in that position,
including king and pawns. |
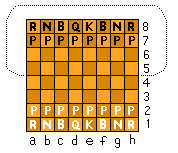
Definition 3. The SPACE of a piece is the number of
squares in
your opponent's half of the board to which the piece can
legally move, excluding the square it currently
occupies.
Opponent's half of the board is encircled in the
figure at the right. |
|
Definition 4. The SPACE of a position is the sum of the
spaces of all pieces in the position, including king
and pawns. |
|
|
Opponent sits here |
| |
You sit here |
|
Classroom exercize: fill in the empty boxes of the table below.
|
piece |
Bishop |
queen |
king |
knight |
rook |
pawn |
Maximum freedom number on
an otherwise empty board. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Locations of piece at which maximum
freedom number is attained |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Note 5. |
Chess positions with larger FREEDOM NUMBERS are more flexible
and more easily changed to take advantage of new ideas and/or
new problems. |
| Note 6. |
Chess positions with larger SPACE are better suited to supporting
an attack on your opponent's king, which usually sits at the
opposite side of the board (encircled in the figure above). |
| Note 7. |
Both FREEDOM and SPACE are more useful tools in the middle game
and opening, and less useful in the endgame, when pieces are fewer
and can move more easily across the board (even the king). |
In class, students must pause 3 times during an actual game to calculate
the FREEDOM NUMBER and SPACE for both themselves and their opponents.
|
move number |
My total
freedom number |
My opponent's total
freedom number |
My total space |
My opponent's
total space |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
This page last updated
28 August 1998 |
|


